Guinea Worm Disease Edges Closer to Extinction:
Guinea Worm Disease Edges
Closer to Extinction:
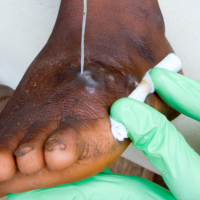
Guinea worm disease is a
debilitating ailment caused by long, thread-like parasites that slowly emerge
from human skin blisters, plaguing sufferers with excruciating pain. The
disease, also known as Dracunculiasis,
is contracted when individuals ingest parasite eggs in contaminated water, with
the worms taking up to a year to incubate before surfacing. Victims often
struggle to carry out daily functions for months due to the severity of the
infection.
Remarkably, Guinea worm disease
is on the brink of eradication, poised to become only the second human
infection eliminated globally after smallpox, thanks to sustained, low-cost
public health initiatives spearheaded by the Carter Center over the past four
decades. In the mid-1980s, over 3.5 million cases of Guinea worm disease were
reported annually across 20 countries, predominantly in South Asia and
Sub-Saharan Africa. However, concerted eradication efforts have led to a
remarkable decline, with only 6 cases reported in 2023, confined to isolated
regions in just four African nations. This progress underscores the efficacy of
grassroots interventions facilitated by international collaborations in
combating neglected diseases, particularly in the absence of commercial
incentives.
Unlike diseases such as smallpox
and polio, which were eradicated through vaccination
campaigns, Guinea worm disease has seen no breakthroughs in medical
treatments or preventive measures over the years. The resilient nature of the
Guinea worm parasite makes it particularly challenging to eradicate, as it
inflicts severe pain on its hosts and exhibits remarkable survival capabilities
within water fleas.
Efforts to combat Guinea worm
disease have relied on cost-effective public health strategies, including the
use of cloth filters for drinking water, larvicide applications in ponds, and
the bandaging of emerging worms to prevent contamination. Additionally,
village-level surveillance, education initiatives, and cash rewards for
reporting cases have played pivotal roles in driving down infection rates.
Although Guinea worm disease
persists in remote regions of South Sudan, Ethiopia, Chad, and Mali, where
political instability and civil unrest pose challenges to eradication efforts,
the significant reduction in cases suggests that complete eradication is
achievable in the near future through continued community-based interventions.
The successful battle against Guinea worm disease serves as a testament to global health equity, demonstrating the effectiveness of affordable solutions tailored to the needs of marginalized rural communities. This victory highlights the potential for outsized gains in health outcomes through the deployment of pragmatic, community-driven interventions, transcending the reliance on costly mainstream interventions like vaccines and antibiotics.
Know More:
Read
daily current affairs in English : Click Here
Read
daily current affairs in Tamil : Click Here
Check
the latest jobs update details : Click Here
Our Achievements:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MLRj6js0X5U
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ung7VREhwYI
Download our Mobile Application: Android Mobile | IOS Mobiles
Our Website's:
https://www.bestlearningcentre.in/
Office Location:
https://goo.gl/maps/9JCNNv3HAkC4b92X7
For any clarification, you may contact us at any time.
Educational Counsellor: 7418968881
Customer Support: 7418978881
Enrol Now for Fresh Batch in UPSC | TNPSC | BANK | SSC | RRB |
POLICE | TNTET | CTET | NDA| CDS | AFCAT | DEFENCE | TANCET | CAT | MAT | ZAT
EXAMS.
Call Admission Desk: 7418968881
Book Free Demo Class Now !
Batches available in ONLINE & OFFLINE